-

-
Find Courses
Collections
Cross-Disciplinary Topic Lists
- About
- Donate
- Featured Sites
This is an archived course. A more recent version may be available at ocw.mit.edu.
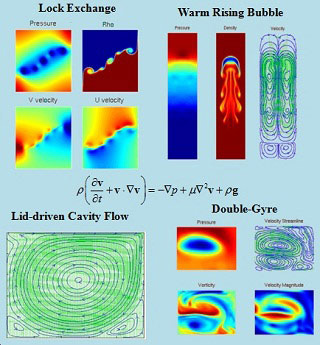
Graphs showing numerical modeling of the following fluid phenomena: lock exchange, warm rising bubble, lid-driven cavity flow, and double-gyre. (Image courtesy of Prof. Pierre Lermusiaux.)
Prof. Pierre Lermusiaux
2.29
Fall 2011
Graduate
This course will provide students with an introduction to numerical methods and MATLAB®. Topics covered throughout the course will include: errors, condition numbers and roots of equations; Navier-Stokes; direct and iterative methods for linear systems; finite differences for elliptic, parabolic and hyperbolic equations; Fourier decomposition, error analysis, and stability; high-order and compact finite-differences; finite volume methods; time marching methods; Navier-Stokes solvers; grid generation; finite volumes on complex geometries; finite element methods; spectral methods; boundary element and panel methods; turbulent flows; boundary layers; Lagrangian Coherent Structures. Subject includes a final research project.
Pierre Lermusiaux. 2.29 Numerical Fluid Mechanics, Fall 2011. (Massachusetts Institute of Technology: MIT OpenCourseWare), https://ocw.mit.edu (Accessed). License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA
For more information about using these materials and the Creative Commons license, see our Terms of Use.